how deep for geothermal energy
How Deep for Geothermal Energy: Exploring the Depths of the Earth
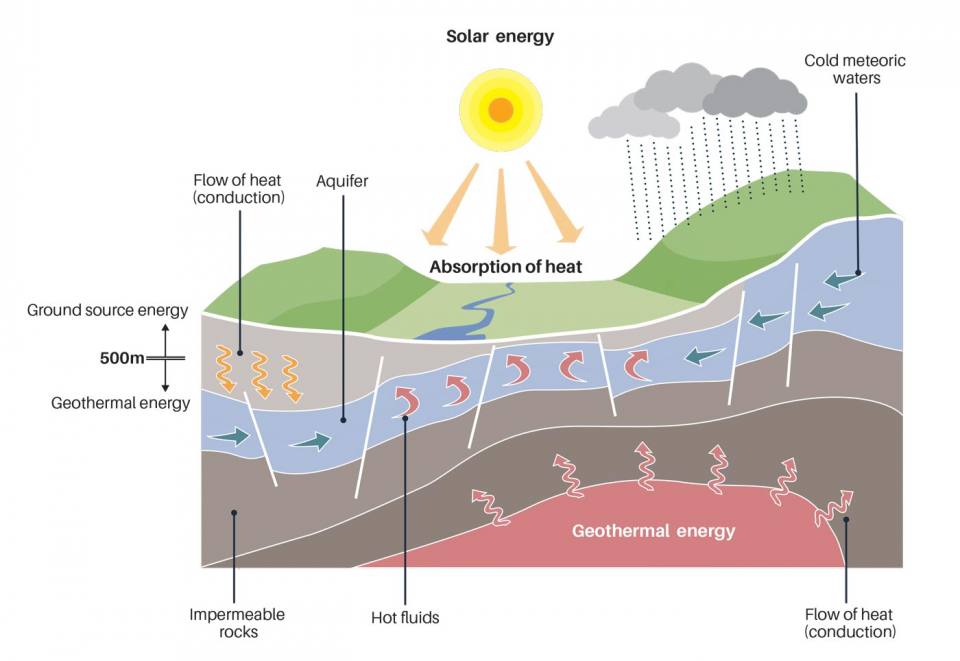 Geothermal energy is a type of renewable energy that has gained increasing attention in recent years. It is a sustainable and eco-friendly source of energy that provides heat and electricity by using the natural heat from the Earth's core. However, the question that arises in the mind of many is - how deep for geothermal energy? In this article, we will explore the answer to this question and provide insights into deep geothermal energy.
Geothermal energy is a type of renewable energy that has gained increasing attention in recent years. It is a sustainable and eco-friendly source of energy that provides heat and electricity by using the natural heat from the Earth's core. However, the question that arises in the mind of many is - how deep for geothermal energy? In this article, we will explore the answer to this question and provide insights into deep geothermal energy.
The Definition of Geothermal Energy
Before delving into the topic of how deep for geothermal energy, it is essential to understand what geothermal energy is. Geothermal energy is a type of renewable energy that utilizes the natural heat of the Earth’s core to produce electricity or heat. It is a sustainable energy source that provides an alternative to conventional sources of energy like fossil fuels and nuclear power.
How Deep for Geothermal Energy?
 The depth of geothermal energy varies depending on different factors such as location, temperature gradient, and permeability of rocks, to name a few. However, in general, it is found at depths ranging from a few meters to several kilometers below the Earth’s surface.
The depth of geothermal energy varies depending on different factors such as location, temperature gradient, and permeability of rocks, to name a few. However, in general, it is found at depths ranging from a few meters to several kilometers below the Earth’s surface.
Shallow Geothermal Energy
Shallow geothermal energy refers to systems that take advantage of the natural heat stored in the shallow ground. Typically, the depth of shallow geothermal systems goes up to 200 meters. It is a commonly used technology for heating and cooling buildings, greenhouses, and other residential and commercial applications.
Deep Geothermal Energy
Deep geothermal energy, also known as high-temperature geothermal energy, refers to systems that extract heat from deeper resources, around 2 to 5 kilometers. It is a more advanced technology that utilizes the Earth’s natural heat to produce electricity. The deeper the geothermal reservoir, the hotter the temperature, and the more energy it can produce. However, the cost of drilling and equipment rises as the depth increases.
Complications in Deep Drilling
 Drilling deep wells for geothermal energy can be a complex and expensive process. The drilling technology used for deep wells must be capable of withstanding high temperatures and pressures found in the Earth’s crust. As the depth increases, the drilling process becomes more challenging, and it requires a specialized team of experts to ensure safety and success.
Drilling deep wells for geothermal energy can be a complex and expensive process. The drilling technology used for deep wells must be capable of withstanding high temperatures and pressures found in the Earth’s crust. As the depth increases, the drilling process becomes more challenging, and it requires a specialized team of experts to ensure safety and success.
Comparisons of Deep Geothermal Energy
 Compared to shallow geothermal systems, deep geothermal energy is a more efficient and cost-effective source of energy. It produces higher temperatures and, in turn, more energy output. Additionally, its footprint is relatively small and does not produce any greenhouse gas emissions, making it a more sustainable and greener alternative to conventional sources of energy like fossil fuels.
Compared to shallow geothermal systems, deep geothermal energy is a more efficient and cost-effective source of energy. It produces higher temperatures and, in turn, more energy output. Additionally, its footprint is relatively small and does not produce any greenhouse gas emissions, making it a more sustainable and greener alternative to conventional sources of energy like fossil fuels.
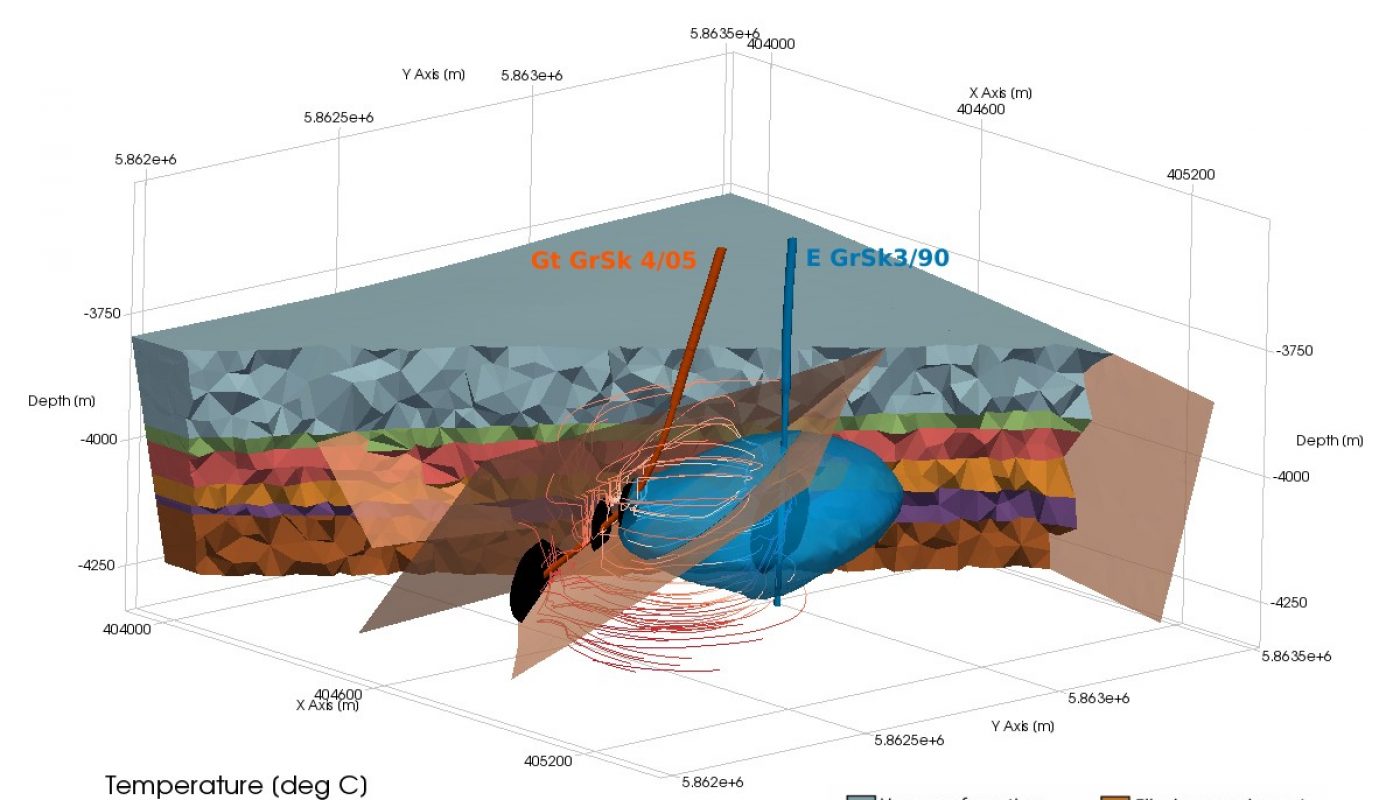 Numerical simulations have found that deep geothermal energy reservoirs are more efficient in terms of energy production, with a production capacity of up to 5 to 10 MW per well.
Numerical simulations have found that deep geothermal energy reservoirs are more efficient in terms of energy production, with a production capacity of up to 5 to 10 MW per well.
FAQs
Q: What is geothermal energy?A: Geothermal energy is a type of renewable energy that utilizes the natural heat of the Earth’s core to produce electricity or heat. Q: How deep for geothermal energy production?
A: It can range from a few meters to several kilometers below the Earth’s surface, depending on various factors. Q: What is shallow geothermal energy?
A: It refers to systems that take advantage of the natural heat stored in the shallow ground, typically up to 200 meters. Q: What is deep geothermal energy?
A: It is an advanced technology that utilizes the Earth’s natural heat to produce electricity, at depths ranging from 2 to 5 kilometers. Q: What are the complications of deep drilling?
A: Drilling deep wells for geothermal energy can be a complex and expensive process, and requires a specialized team of experts to ensure safety and success.
The Tutorial on How Deep for Geothermal Energy
If you are considering geothermal energy as an alternative source of power for your home or business, it is important to evaluate the costs, benefits, and requirements of the system. Here are some steps that can help you understand how deep for geothermal energy:
- Choose a reliable and experienced company that specializes in geothermal energy systems.
- Conduct a site survey to evaluate the geological characteristics and temperature gradient of the site.
- Determine the depth of the geothermal resource and the type of system (shallow or deep) that is most suitable for the location.
- Assess the installation costs, including drilling and equipment costs.
- Calculate the return on investment and the payback period for the system.
- Maintain the system regularly to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Recent Facts about How Deep for Geothermal Energy
 Here are some recent facts about how deep for geothermal energy:
Here are some recent facts about how deep for geothermal energy:
- Geothermal energy currently accounts for 3.7% of global electricity production, and it is expected to grow by 1% per year.
- The global geothermal power capacity is expected to reach 18.4 GW by 2025.
- The United States is currently the largest producer of geothermal energy, with an installed capacity of 3.8 GW.
- The cost of geothermal energy has decreased by more than 20% since 2010 due to technological advancements and market competition.
- Deep geothermal energy has the potential to produce up to 10% of Europe’s electricity demand by 2050.
Advantages and Disadvantages of How Deep for Geothermal Energy
Like any other energy source, geothermal energy has its advantages and disadvantages. Here are some of them:
Advantages:- Geothermal energy is a sustainable and renewable energy source.
- It has a relatively low carbon footprint, as it does not produce any greenhouse gas emissions.
- It has a constant and reliable source of energy that is not dependent on weather conditions.
- It has a low operating cost, as it requires minimal fuel and maintenance costs.
- It has a long lifespan, with some geothermal plants lasting up to 50 years.
Disadvantages:
- It requires high initial investment costs, particularly for deep geothermal systems.
- It is location-specific, as it requires specific geological formations and temperature gradients.
- It can cause subsidence and seismic activity in some cases.
- It has limited availability in some regions, as not all nations have favorable geology for geothermal energy production.
- It has potential environmental impacts, such as the release of hydrogen sulfide and other gases from the geothermal fluid.
Conclusion
As the world is embracing a greener and sustainable future, geothermal energy has emerged as a promising source of power. From